Sodium Starch Glycolate is a kind of high molecular organic compound, which is obtained by the cross-linking reaction of potato starch and sodium chloroacetate in ethanol solution, then Carboxymethylation of cross-linked starch in alkaline medium with sodium chloroacetate, and finally neutralization with citric acid.

Carboxymethylstarch sodium is widely used in medicine. As far as pharmaceutical preparations are concerned, it can replace gelatin as raw materials for making capsules, tablets and icing. It has strong water absorption and expansibility, can bubble up quickly in cold water, and after water absorption, the particles expand but do not dissolve, do not form colloidal solution, do not hinder the continuous infiltration of water and affect the further disintegration of tablets. Therefore It can be used as an efficient disintegrating agent and excipient for insoluble drugs and soluble drug tablets.
Chloroacetic acid is a kind of strong acid, which has strong stimulation and corrosiveness. It can usually enter human body through respiratory system, digestive system and skin, causing damage to skin, liver, kidney, heart and other organs, even causing acute poisoning and death in high concentration. Modern medicine has proved that chloroacetic acid is triphylactic, so it is necessary to control its residue.
According to the requirements for the determination of Sodium Starch Glycolate in Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020, the content of chloroacetic acid in Sodium Starch Glycolate can be determined by ion chromatography, SHINE CIC-D100 ion chromatograph, SH-AC-11 column, conductivity detector and clarity workstation.
1.Instrument conditions and experimental parameters

SHINE CIC-D100 ion chromatograph
Instrument: CIC-D100
Column: SH-AC-11
Eluent: 10mM KOH
Flow rate: 1.0mL / min
Detection method: suppressed conductivity method
Injection volume: 25uL
Column temperature:35℃
Suppression current: 30 mA
2.Reagents and standard solutions
1. Chloroacetic acid standard solution: certified standard solution
2. Ultra pure water: resistivity ≥ 18.25mΩ·cm (25℃)
3. Sodium hydroxide: super pure
3.Sample pretreatment and determination
1 Test solution: take about 0.5g of the sample, weigh it precisely, put it in a 50mL centrifuge tube, add water appropriately, shake it for about 1 minute, centrifuge, transfer the supernatant quantitatively to a 25mL volumetric flask, extract the residue two times with the same method of water, combine the supernatant to the same 25mL volumetric flask, dilute it with water to the moment, shake it up, filter it, and take the continuous filtrate as the test solution;
2 Control solution: take about 50mg of chloroacetic acid control, accurately weigh it, place it in a 50ml measuring bottle, dilute it to the scale with water, accurately measure a proper amount, dilute it with water to make a solution containing 40 μ g of chloroacetic acid per 1ml;
3 System suitability solution: take appropriate amount of chloroacetic acid and sodium chloride, dissolve and dilute with water to make a mixed solution containing 2 μ g each in 1ml.
The system suitability solution, chloroacetic acid control sample and carboxymethyl starch sodium test sample were analyzed through 0.22 μ M filter membrane respectively.
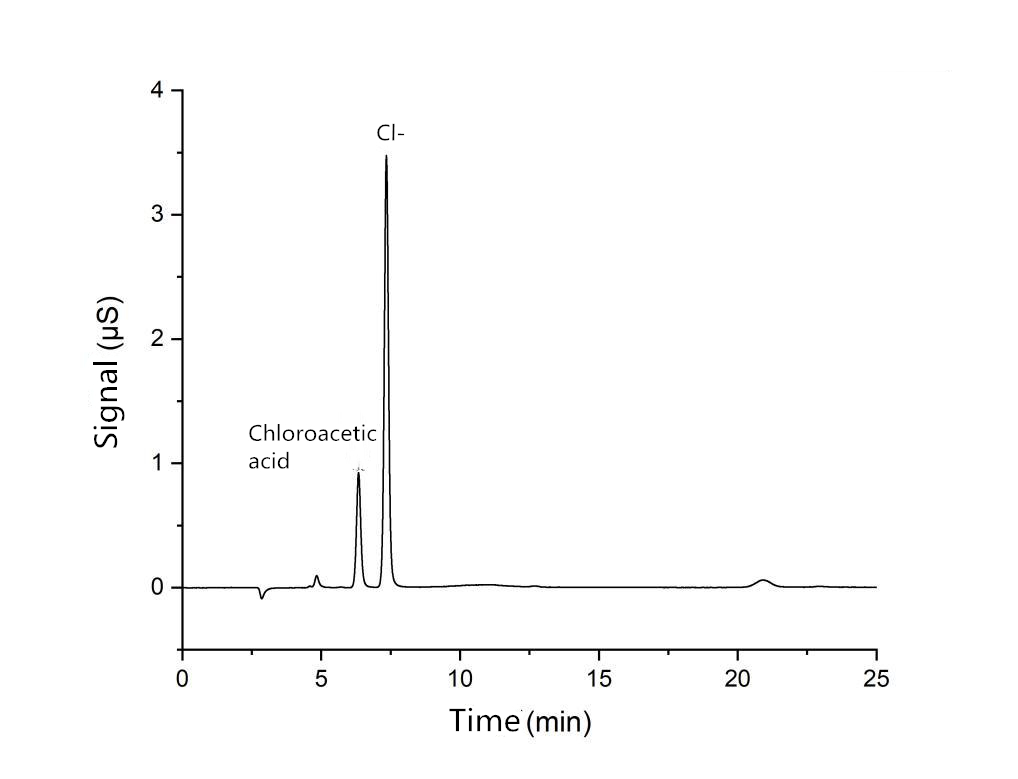
System suitability solution spectrum
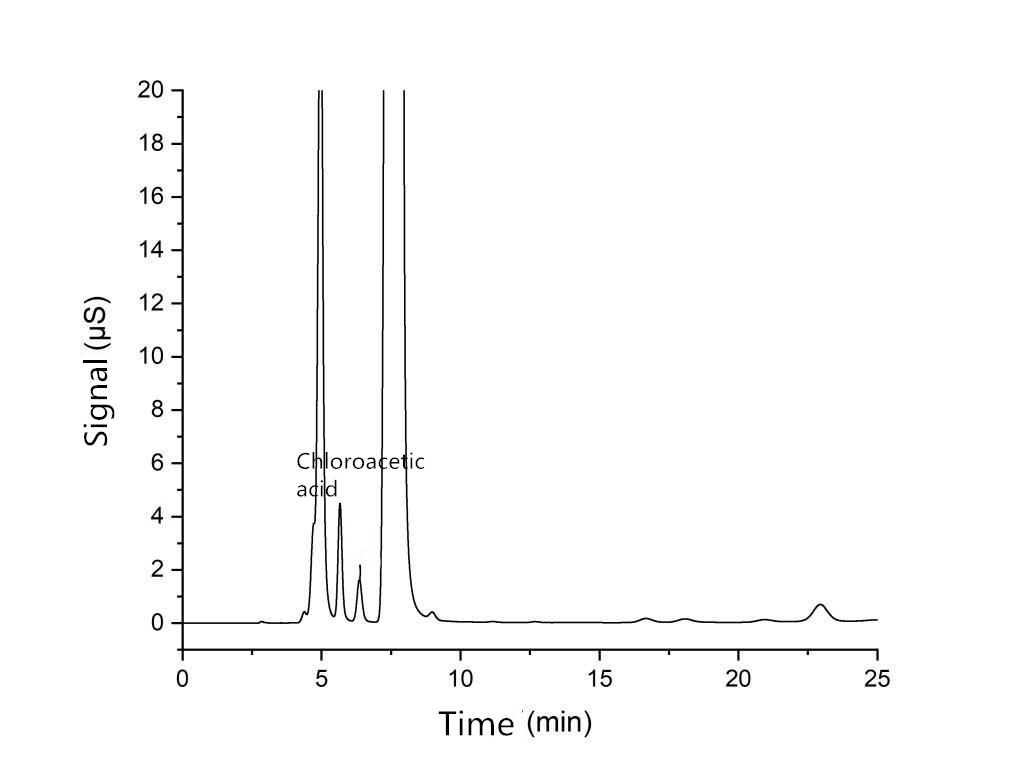
Test sample spectrum
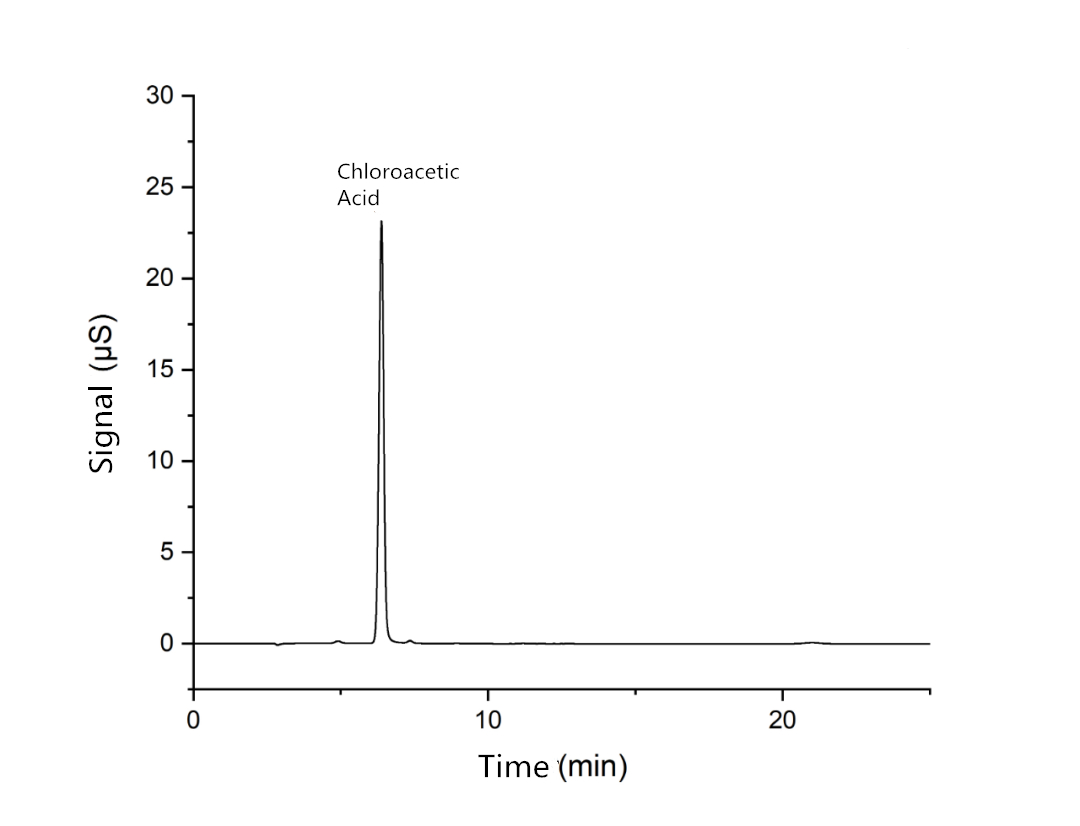
Reference spectrum
Test result
Sample name | Test items | Measured value |
System suitability solution
| Resolution of chloroacetic acid and Cl- R | 3.42
|
Test solution
| Chloroacetic acid concentration (mg /L) | 3.003 |
Sodium Starch Glycolate | Mass fraction of chloroacetic acid (%)
| 0.015 |