In recent years, the use of chemical fertilizer in China has increased gradually. The use of fertilizer can increase the fertility of soil, provide better nutrition environment for plant growth, and improve the yield and quality of agricultural products, but improper application of fertilizer also brings a lot of environmental impact.

The common trace ions in fertilizer are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, nitrite, iodine and other inorganic anions. Their excessive existence will not only affect the growth of crops, but also bring a lot of harm to soil, environment and even human health. If the chloride ion is excessive, the soil will harden and the crops will die; after the nitrite is absorbed by the crops and absorbed by the human body, it will lead to methemoglobinopathy, etc.
Standard GBT 29400-2012, Sn / T 0736.14-2011 specifies the determination method of anions in fertilizer. In order to accurately quantify the inorganic anions in fertilizer, reduce the environmental harm to water source and soil, ensure the normal growth and safety of crops, and maintain the health of consumers, the ion chromatography conductivity method was established to detect the anions in fertilizer.
The method has the advantages of safety, accuracy, simple operation, low detection limit and good reproducibility. It can eliminate the interference of coexisting ions, and each ion can be separated well. It is suitable for the detection of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, nitrite, nitrate, phosphate and iodine ions in fertilizer.
Weigh 0.25g of dried and smashed chemical fertilizer samples for sale in a 100ml volumetric flask, add pure water to a constant volume, shake them up, and then treat them with ultrasonic for 30min. Take part of the solution and centrifugate it for 10min at a speed of 8000r / min. take the centrifuged supernatant with a syringe and pass it through a 0.22 μ m water needle filter membrane. Then slowly push the sample solution into the activated C18 solid-phase extraction column and Ba solid-phase extraction column. The injection speed is less than 3mL/min, discard the first 5ml of solution.

Chromatographic conditions
Instrument: CIC-D150
Column: SH-AP-1
Eluent: 0-10min 14mM KOH
10-25min 14-25mM KOH
25.1min 14mM KOH
Flow rate: 0.8mL / min
Column pressure: 10.1Mpa
Detection method: suppressed conductivity method
Injection volume: 25uL
Column temperature:35℃
Suppression current: 80 mA
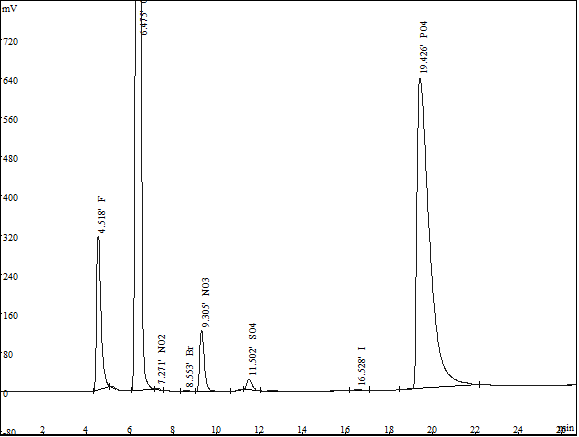
Spectrogram